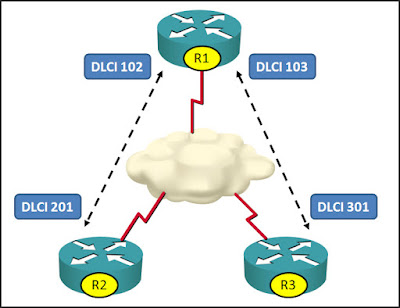
Con esta practica en GNS3, verificaremos y entenderemos el funcionamiento de Frame Relay. Esta tecnologia WAN (Wide Area Network) es muy popular porque facilita la construcción de redes confiables y de bajo costo. Uno de sus principales ventajas es de poder configurar enlaces seriales punto a punto con la capacidad de conectar un sitio a muchos sitios remotos a través de un circuito físico. En esta practica se mostrara el proceso de la configuración de Frame Relay utilizando la siguiente topologia.
Topologia de Frame Relay a Configurar en GNS3.
La imagen anterior muestra una topologia Full Mesh. Una red Mesh es una red múltiplemente conexa, en la cual los nodos tienen más de una conexión con más de un nodo diferente. No necesariamente deben conectarse todos contra todos, éste es un caso especial que se denomina Full-Mesh. Configuraremos esta topologia en GNS3, en el cual utilizaremos un Router central el cual le configuraremos cuatro interfaces seriales donde le indiciaremos los DLCIs para que puedan ser asignados dinamicamente con Inverse ARP. Al configurar la encapsulacion Frame Relay en cada Router, automaticamente detectara los DLCIs ya que Inverse ARP esta habilitado por defecto.
Frame Relay en GNS3 con topologia Full Mesh.
Para configurar esta toplogia primero realizaremos la configuracion del Switch de Frame Relay, donde le indicaremos los DLCIs. Lo primero es activar la conmutación Frame Relay en el Router con el siguiente comando.
FrameRelay(config)#frame-relay switching
Luego a configurar las interfaces seriales, la encapsulacion, el reloj, le indicaremos que la interface como dispositivo DCE y por ultimo definimos los DLCIs para cada interface.
FrameRelay#configure terminal
FrameRelay(config)#interface Serial1/0
FrameRelay(config-if)#no ip address
FrameRelay(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
FrameRelay(config-if)#clock rate 64000
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay intf-type dce
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 102 interface Serial1/1 201
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 103 interface Serial1/2 301
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 104 interface Serial1/3 401
FrameRelay(config-if)#no shutdown
FrameRelay(config-if)#exit
FrameRelay(config)#interface Serial1/1
FrameRelay(config-if)#no ip address
FrameRelay(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
FrameRelay(config-if)#clock rate 64000
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay intf-type dce
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 201 interface Serial1/0 102
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 203 interface Serial1/2 302
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 204 interface Serial1/3 402
FrameRelay(config-if)#no shutdown
FrameRelay(config-if)#exit
FrameRelay(config)#interface Serial1/2
FrameRelay(config-if)#no ip address
FrameRelay(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
FrameRelay(config-if)#clock rate 64000
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay intf-type dce
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 301 interface Serial1/0 103
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 302 interface Serial1/1 203
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 304 interface Serial1/3 403
FrameRelay(config-if)#no shutdown
FrameRelay(config-if)#exit
FrameRelay(config)#interface Serial1/3
FrameRelay(config-if)#no ip address
FrameRelay(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
FrameRelay(config-if)#clock rate 64000
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay intf-type dce
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 401 interface Serial1/0 104
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 402 interface Serial1/1 204
FrameRelay(config-if)#frame-relay route 403 interface Serial1/2 304
FrameRelay(config-if)#no shutdown
FrameRelay(config-if)#exit
FrameRelay(config)#end
FrameRelay#
Ahora configuramos las interfaces de los Routers.
R1>enable
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)# interface serial1 /0
R1(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
R1(config-if)#frame-relay lmi-type cisco
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#end
R1#
R2>enable
R2#configure terminal
R2(config)#interface serial1/0
R2(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
R2(config-if)#frame-relay lmi-type cisco
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#end
R2#
R3>enable
R3#configure terminal
R3(config)#interface serial1/0
R3(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
R3(config-if)#frame-relay lmi-type cisco
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#end
R3#
R4>enable
R4#configure terminal
R4(config)#interface serial1/0
R4(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
R4(config-if)#frame-relay lmi-type cisco
R4(config-if)#ip address 192.168.123.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
R4(config-if)#end
R4#
Terminando de realizar lo anterior ya podemos verificar en cualquier router con el comando show frame-relay pvc que Inverse ARP ha realizado su trabajo.
R1#show frame-relay pvc
PVC Statistics for interface Serial1/0 (Frame Relay DTE)
Active Inactive Deleted Static
Local 3 0 0 0
Switched 0 0 0 0
Unused 0 0 0 0
DLCI = 102, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial1/0
input pkts 1 output pkts 1 in bytes 34
out bytes 34 dropped pkts 0 in pkts dropped 0
out pkts dropped 0 out bytes dropped 0
in FECN pkts 0 in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0
out BECN pkts 0 in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 1 out bcast bytes 34
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
pvc create time 00:07:06, last time pvc status changed 00:06:46
DLCI = 103, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial1/0
input pkts 1 output pkts 2 in bytes 34
out bytes 68 dropped pkts 0 in pkts dropped 0
out pkts dropped 0 out bytes dropped 0
in FECN pkts 0 in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0
out BECN pkts 0 in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 2 out bcast bytes 68
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
pvc create time 00:07:10, last time pvc status changed 00:06:50
DLCI = 104, DLCI USAGE = LOCAL, PVC STATUS = ACTIVE, INTERFACE = Serial1/0
input pkts 1 output pkts 1 in bytes 34
out bytes 34 dropped pkts 0 in pkts dropped 0
out pkts dropped 0 out bytes dropped 0
in FECN pkts 0 in BECN pkts 0 out FECN pkts 0
out BECN pkts 0 in DE pkts 0 out DE pkts 0
out bcast pkts 1 out bcast bytes 34
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
pvc create time 00:07:11, last time pvc status changed 00:06:41

Muestra estadísticas acerca de los PVC para las interfaces.
Como podemos ver, Inverse ARP ha detectado los DLCIs. Como se muestra en la salida anterior ha detectado 3 DLCIs en funcionamiento. Estas DLCIs son las que tenemos en nuestra topologia. Para verificar el funcionamiento de Frame Relay podemos también utilizar los siguientes comandos.
Las Estadisticas de los LMI.
R1#show frame-relay lmi
LMI Statistics for interface Serial1/0 (Frame Relay DTE) LMI TYPE = CISCO
Invalid Unnumbered info 0 Invalid Prot Disc 0
Invalid dummy Call Ref 0 Invalid Msg Type 0
Invalid Status Message 0 Invalid Lock Shift 0
Invalid Information ID 0 Invalid Report IE Len 0
Invalid Report Request 0 Invalid Keep IE Len 0
Num Status Enq. Sent 140 Num Status msgs Rcvd 115
Num Update Status Rcvd 0 Num Status Timeouts 25
Last Full Status Req 00:00:00 Last Full Status Rcvd 00:00:00
El mapeo de los DLCIs.
R1#show frame-relay map
Serial1/0 (up): ip 192.168.123.2 dlci 102(0x66,0x1860), dynamic,
broadcast,, status defined, active
Serial1/0 (up): ip 192.168.123.3 dlci 103(0x67,0x1870), dynamic,
broadcast,, status defined, active
Serial1/0 (up): ip 192.168.123.4 dlci 104(0x68,0x1880), dynamic,
broadcast,, status defined, active0
Muestra las entradas de mapeo actuales.
En la salida anterior nos muestra los DLCIs y que han sido aprendidos de manera dinámica. Con el siguiente comando podemos verificar que estamos utilizando la encapsulación de frame-relay en la interface, los datos de LMI, los Keepalive y mas informacion sobre la interface.
R1#show interface serial1/0
Serial1/0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is M4T
Internet address is 192.168.123.1/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation FRAME-RELAY, crc 16, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Restart-Delay is 0 secs
CRC checking enabled
LMI enq sent 105, LMI stat recvd 80, LMI upd recvd 0, DTE LMI up
LMI enq recvd 0, LMI stat sent 0, LMI upd sent 0
LMI DLCI 1023 LMI type is CISCO frame relay DTE
FR SVC disabled, LAPF state down
Broadcast queue 0/64, broadcasts sent/dropped 5/0, interface broadcasts 0
Last input 00:00:06, output 00:00:06, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:18:53
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 0/1/256 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1158 kilobits/sec
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
85 packets input, 1618 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
114 packets output, 1671 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
1 carrier transitions DCD=up DSR=up DTR=up RTS=up CTS=up

Encapsulacion Frame Relay en la Interface Serial.
Verificamos la conectividad dando un ping a cada router.
R1#ping 192.168.123.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.123.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/142/332 ms
R1#ping 192.168.123.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.123.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/120/192 ms
R1#ping 192.168.123.4
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.123.4, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/127/240 ms